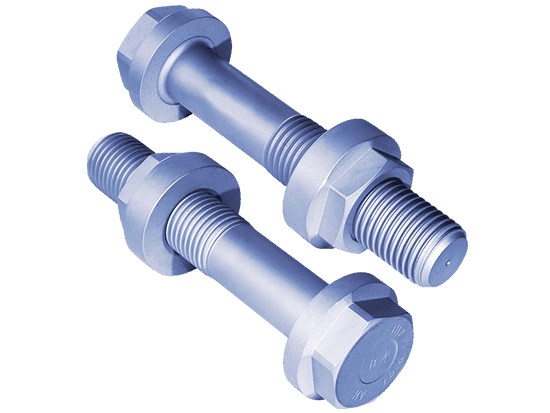

A nut is a small metal object with a hole in the middle that has a corrugated hole. These curved holes are known as threads. Nuts are used as a fastening device. It is important to note that evens though nuts are used as a fastening device, they cannot be used without bolts. Nuts and Bolts are usually used together to fasten multiple parts together. They are put together on the opposite ends of the material that needs to be fastened, and then tightened through tools such as screwdrivers and allen keys. Screws are a bit different in that sense. They are only single pieces and are used to hold things together. The screw is usually tightened into materials and makes them hold the surface.
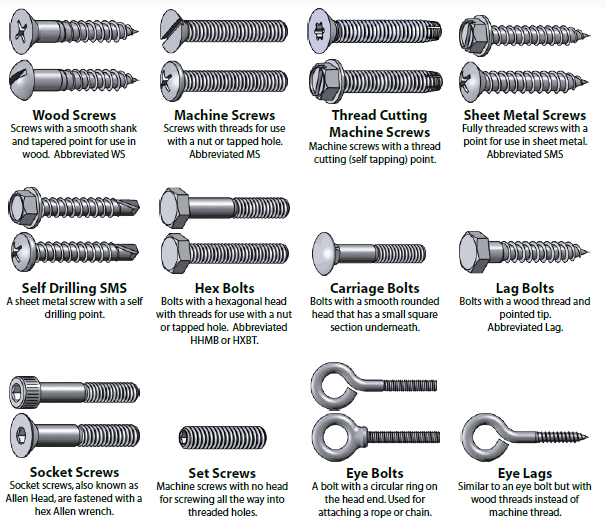
Types of screws
How to use
Nuts and bolts are held together by a combination of friction of their thread, a slight stretch of the bolt, & compression of the part to join together. For nuts and bolts, they should be kept apart first, then the bolt should be inserted into the materials that need to be fastened. Thereafter, the bolt should be inserted from the other end and should be tightened with the bolt. The nuts come with a separate locking mechanism that prevents machine parts from loosening due to the vibration of the parts or parts that they joined. The nut has internal threads so that it can be tightened easily on the bolt. Screws can directly be impacted upon a surface and then tightened enough to ensure they’re fixed properly. The parts connected with the screw have less strength than the bolt.
Common applications
1. All types of industrial equipment
2. Solar thermal plant & Nuclear power plant
3. Sewage Treatment plant
4. Pumps and valves
5. Transportation and storage, pressure vessels, tanks, piping, & heat exchangers
Some example tasks that students can try out in the ATL Lab
1. Tightening the screw on a ply
2. Fasten two plies together with nut and bolt
Important Links for more details
How to use nut and bolts – ( )
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XwAB6-pH4LQ
Difference between Bolts and screws –
https://monroeengineering.com/blog/bolts-vs-screws-whats-the-difference/
Safety Tips and Precautions
● Tighten Bolts For Maximum Strength – The users see the tensile force only, not the comprehensive force. The bolt has an internal reaction force for which it is itself in the tension, which is equal to the amplitude of compression force.
● Avoid Over-Tightening – It is difficult to determine the load that a fastener is bearing during clamping, but it is necessary to stay away from the point of over-tightening. It is important to manage the right balance for the perfect clamping.
● Change The Melted Head Screws – At the time of sudden uncertainties, removing the melted screws is nothing but calling the fires for your own. Therefore, it’s better to be prepared; replacing these with new ones can save you from blunders.


