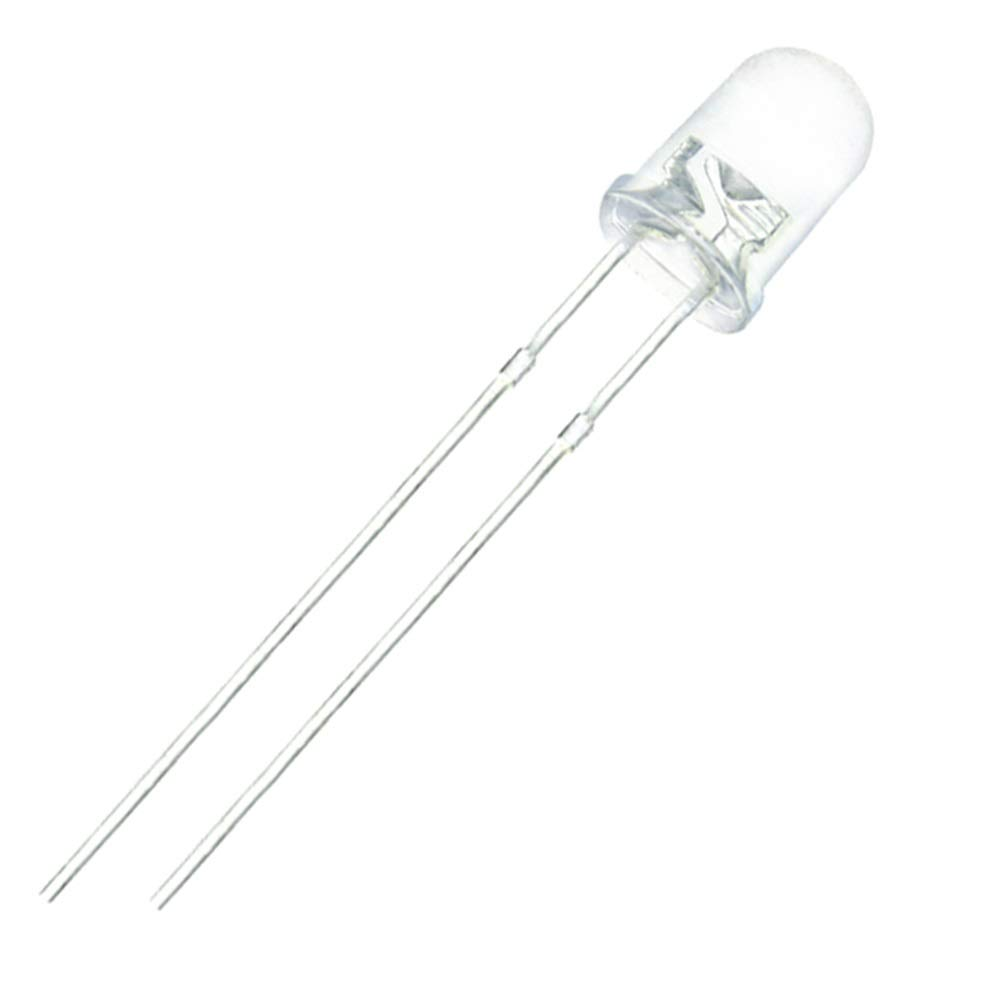
LED (Light Emitting Diode) is a diode which when connected in forward bias generates light. The light generated depends on the colour for which the LED is designed.
A LED contains two leads – positive terminal (longer one) and negative terminal (shorter one). LED will glow when postive pin of LED is connected to +ve terminal of the battery and negative pin of LED is connected to -ve terminal of the battery. The operating voltage of an LED is between 1.8 and 3.3 volts
How to use
To make a simple connection, we can connect the LED with a battery to make it glow. The positive lead of the LED needs to be connected to the positive terminal of the battery, and negative lead to the negative terminal. We need to make sure that the voltage rating matches the battery voltage. Otherwise, we can use resistors to provide the required voltage.
Common Applications
1. To provide light
2. As indicators
Some example projects that students can try out in the ATL Lab
1. Create a simple circuit to glow an LED – https://youtu.be/BS9IgyAp3I0
2. Connect LEDs in series with the battery and resistors and observe the dip in the intensity of light as the number of leds increase
Safety Measures to follow
1. Don’t put the LED close to the eyes.
2. Supplying a high voltage might damage the LED.
Important Links
1. All about LEDs –
https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/light-emitting-diodes-le
2. How does a LED work at the micro level (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=No8PZsLnjZU)
YouTube Video


