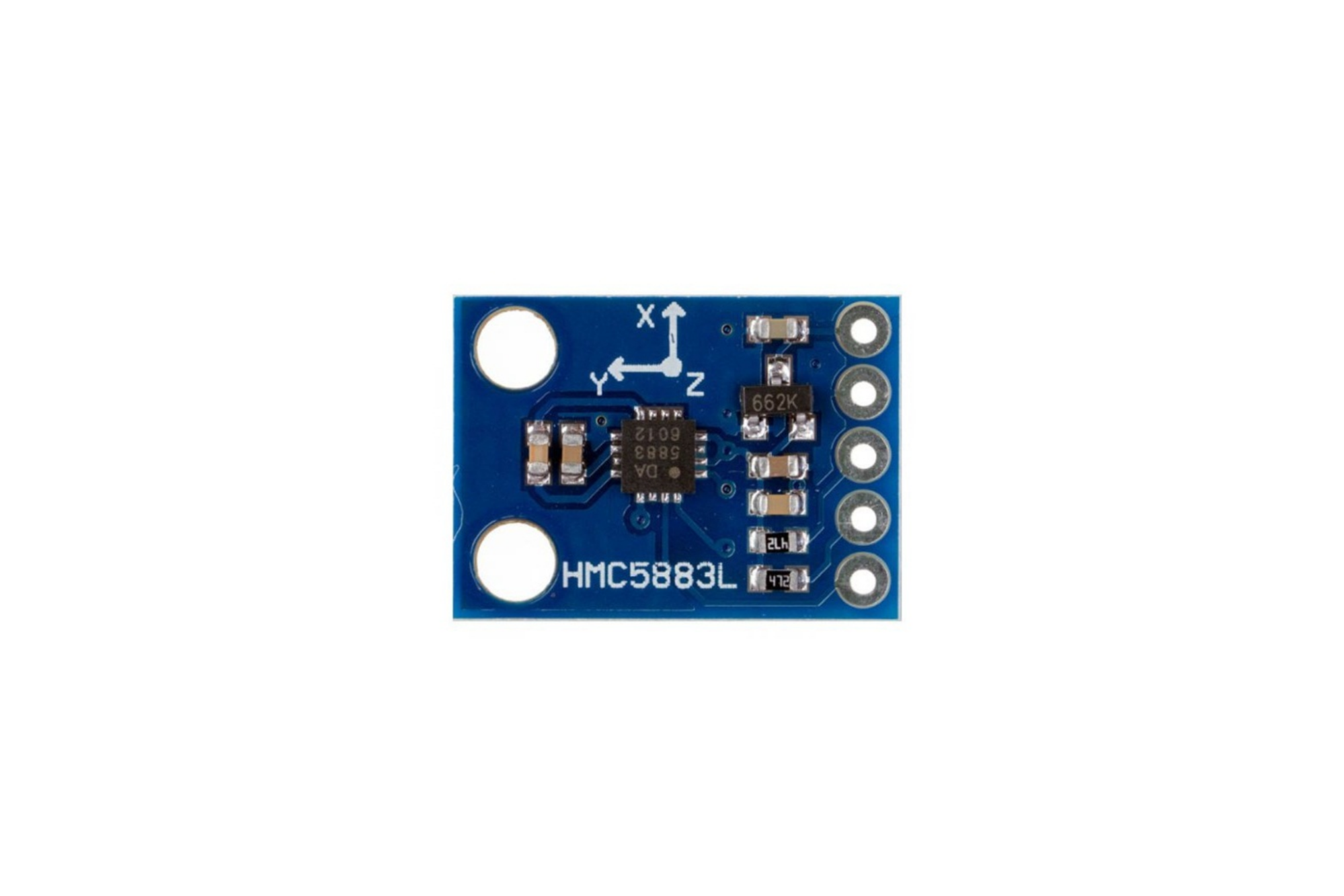
A magnetometer is used to find directions, by aligning itself with the earth’s magnetic field. There are many types of magnetometers such as fluxgate, magnetoresistive, magneto-inductive and others.
Earth’s magnetic field is present in space which points towards the magnetic north. Current carrying conductor also generates a magnetic field around itself. Hence, whenever a current carrying conductor is placed in space, it experiences the effect of the earth’s magnetic field affecting the flow of the electrons through that conductor. These changes in the flow of the electrons are used for identifying the heading or direction of the magnetic field. This is the basic working principle of the magnetometer. The HMC5883L uses a magnetoresistive sensor arranged in a bridge circuit, which is made of nickel-iron (Ni-Fe magnetic film) material. A HMC5883L module has 5 pins:- VCC, GND, SCL, SDA, and DRDY
How to use
Tutorial –
https://electronoobs.com/eng_arduino_tut77.php
Common Applications
1. Used to detect orientation of mobile phones.
2. Used in digital compasses.
Some example projects that students can try out in the ATL Lab
1. Make a compass using magnetometer (https://youtu.be/k6ccH8QYGK8) YouTube Video
Safety Measures to follow
1. Any sort of external magnetic force would distort the readings of the magnetometer.
Important Links
1. How does a magnetometer work (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0kgw_P5q9_o)
YouTube Video