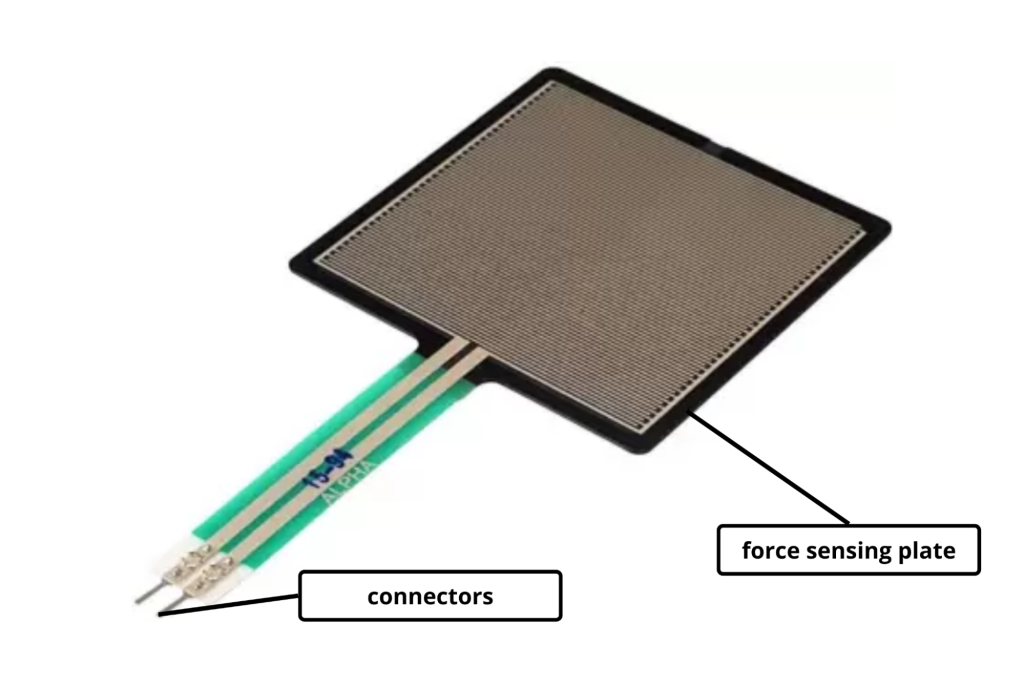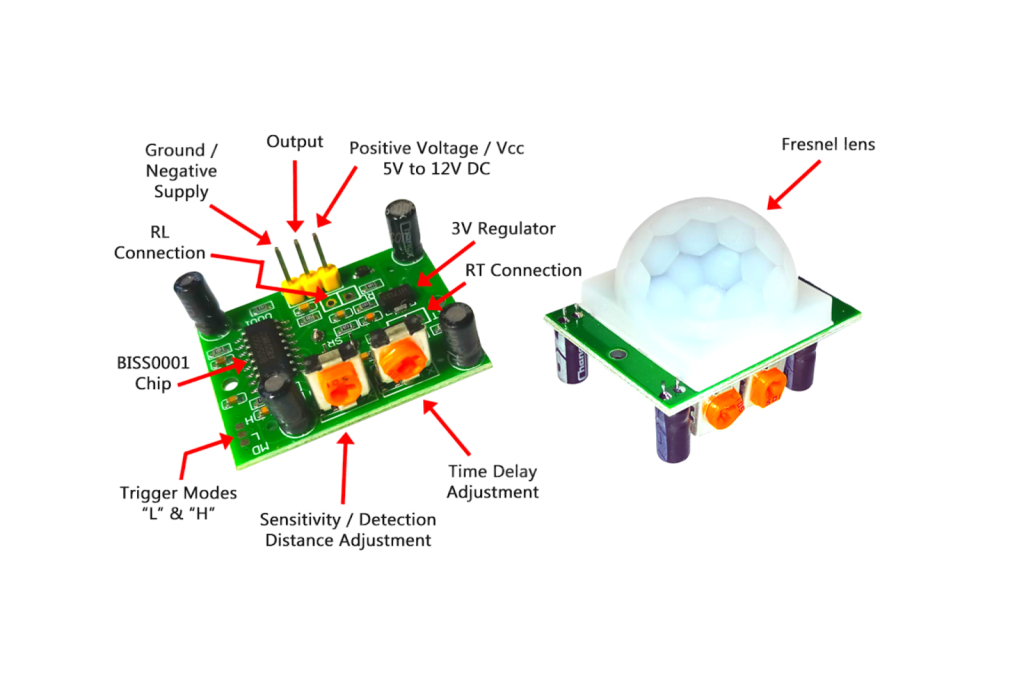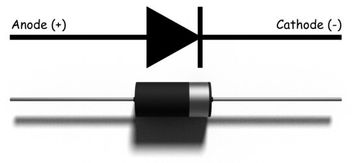
A diode is a semiconductor device that essentially acts as a one-way switch for current. It allows current to flow easily in one direction, but severely restricts current from flowing in the opposite direction. This property of a diode is very useful in certain scenarios where we only want the current to flow unidirectionally.
Components
A diode generally has two terminals, anode and cathode. It conducts electricity only in one direction, which means, it acts as an insulator if current is in a specific direction or as conductor if the direction of flow of current is reversed. So, it can be made to use by connecting to the circuit.
How to use
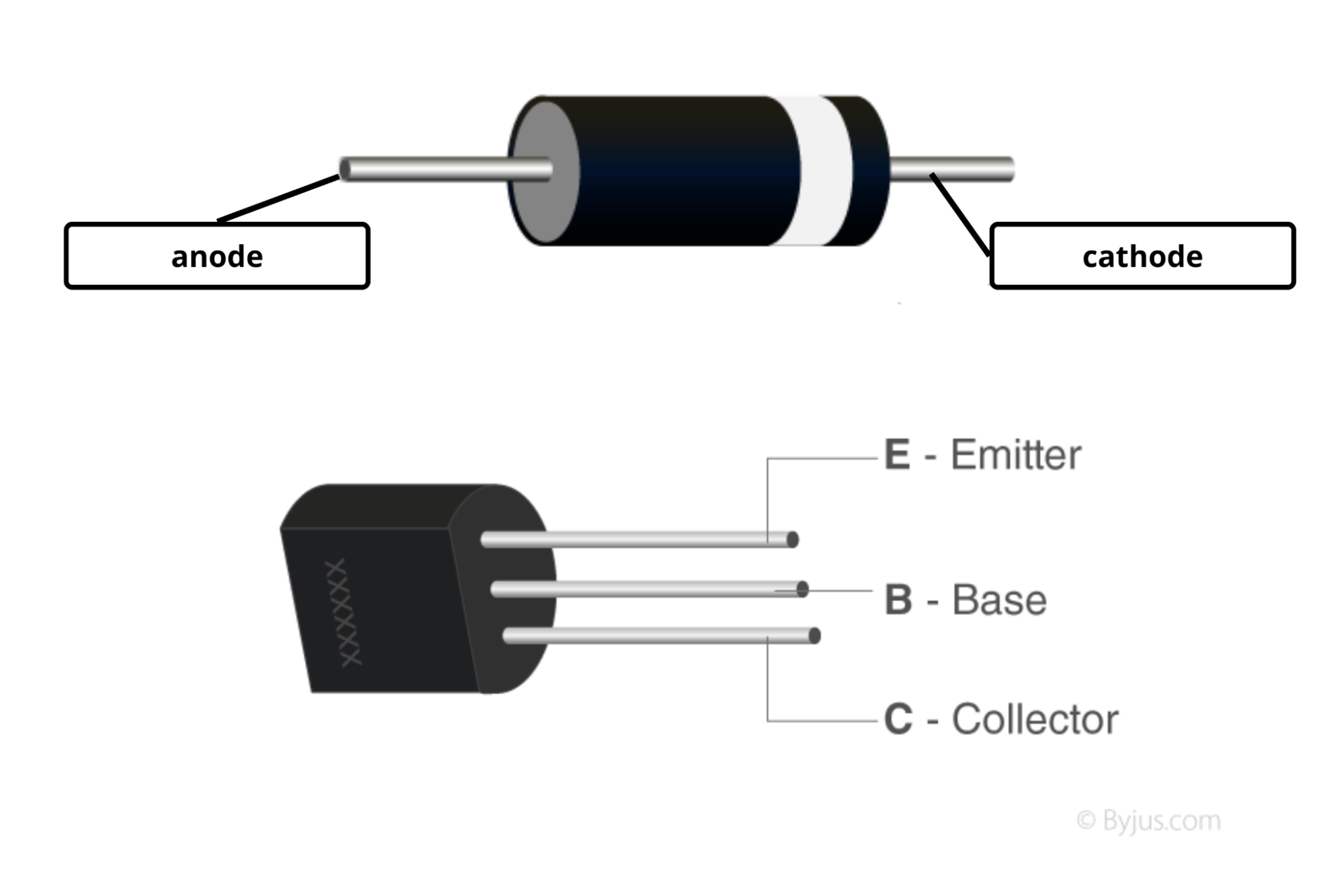
Diode
A diode has 2 terminals, it can be made to use by connecting in series to the circuit. A LED is also a type of diode, which we know is connected along the circuit to work. Similarly, we shall connect other diodes too, to make them work.
Tutorial –
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=c08_K3ytvGI
Common Applications
● Diodes are used in many appliances such as LED, rectifiers, switches, solar cells, etc
● Diodes are also used in rectifier, clipper and clamper circuits
Some example projects that students can try out in the ATL Lab
● Make a rectifier using diodes –
https://www.elprocus.com/rectifier-diode-working-applications/
● Create a Clipper using diodes –
https://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/diode/diode-clipping-circuits.html
Safety Measures to follow
● Do not let the soldering touch the glass body of the diode directly while making connections.
● Don’t use higher voltages on diodes more than the specified limits (0.60V – 0.75 V).
Important Links
1. Overview of Diodes –